The talent management landscape has fundamentally shifted. While traditional HR functions once relied on manual processes and intuition, AI can boost staff retention by 51%, improve employee performance by 27%, and increase employee satisfaction by 24%. Organizations are no longer experimenting—they’re implementing at scale.
Current State of AI Adoption in Talent Management
76% of HR professionals believe AI will significantly impact their field, with 38% of HR managers already using AI tools to improve talent management and boost organizational productivity. The numbers tell a compelling story: approximately 50% of organizations worldwide have integrated AI tools into their HR departments for various functions like recruitment, performance management, and employee engagement.
The shift from pilot programs to production systems marks 2025 as the inflection point. 67% of organizations use AI in recruitment, with enterprise companies leading at 78%, representing 189% growth since 2022. This isn’t gradual adoption—it’s transformation at velocity.
Regional Differences Matter
North America leads AI adoption in HR, with 68% of HR departments using AI tools, Europe follows at 54%, while Asia lags at 45%. Yet both the U.S. and India have doubled their AI/Automation workforce year over year, signaling rapid catch-up in emerging markets.
The Strategic Imperative: Why Now?
Josh Bersin, HR industry analyst and founder of The Josh Bersin Company, declared at UNLEASH World 2025 that AI is going beyond transforming HR and the world; it is reinventing it. This isn’t hyperbole—it’s observable reality.
Traditional talent management faces critical bottlenecks:
Time drain on high-value activities: A study by Talent Board And Phenom found that AI-powered screening tools can reduce the time spent on résumé reviewing by up to 75%. Recruiters spend their days on administrative tasks instead of relationship-building.
Skills gap crisis: 60% of employees report insufficient training for core job skills. Organizations lack systematic approaches to identify and close capability gaps.
Retention challenges: Traditional methods fail to predict attrition until exit interviews, when it’s too late.
Bias in decision-making: Human judgment, while valuable, introduces unconscious bias at every stage of the talent lifecycle.
AI addresses each of these systematically, not theoretically but demonstrably. Organizations using AI-powered recruitment tools report 35% faster hiring times and 50% improvement in quality of hire metrics.
Core AI Technologies Powering Talent Management
Machine Learning for Pattern Recognition
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical hiring data, performance metrics, and career trajectories to predict success. AI screening tools achieve 89-94% accuracy rates, with resume parsing at 94% and skill matching at 89% accuracy. These aren’t marginal improvements over manual screening—they’re order-of-magnitude leaps.
Example: A global pharmaceutical company uses ML to match candidates with roles based on skill profiles rather than keywords. Their quality-of-hire scores increased 43% within 18 months, while time-to-fill decreased by 28 days on average.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Understanding Context
NLP extracts insights from unstructured data—performance reviews, interview notes, employee surveys. It identifies sentiment, skill gaps, and career aspirations that manual review would miss.
Predictive Analytics for Forward-Looking Decisions
64% of organizations use predictive models for performance forecasting. These systems forecast retention risk, identify flight-risk employees, and recommend interventions before problems materialize.
Agentic AI: The Next Frontier
By 2028, at least 15% of day-to-day work decisions will be made autonomously by agentic AI compared with zero percent last year. Piyush Mehta, CHRO at Genpact, states that “Agentic AI will take over more workplace tasks, creating opportunities for people managers to focus on strategic, value-added roles in talent engagement and retention”.
AI-Driven Talent Acquisition: From Sourcing to Onboarding
Intelligent Candidate Sourcing
AI scans job boards, social networks, and professional databases simultaneously, identifying passive candidates who match role requirements. It analyzes work history patterns, skill adjacencies, and career progression trajectories that human recruiters might overlook.
Example: A fintech startup used AI sourcing tools to identify candidates from non-traditional backgrounds—former military personnel with transferable cybersecurity skills. Their candidate pool expanded 340%, and diversity hiring increased 67%.
Automated Resume Screening and Ranking
57% of HR professionals report using AI-based tools for recruiting, with 35% specifically using AI for resume screening and automated interview scheduling. These systems parse resumes, extract relevant qualifications, and rank candidates against job requirements in seconds.
Critical consideration: 67% of organizations report ongoing challenges with AI bias management. McKinsey’s behavioral design research shows that organizations combining AI with structured human oversight achieve 73% better fairness outcomes.
Bias Mitigation: From Theory to Practice
Organizations implementing AI responsibly follow structured approaches:
- 43% of companies provide bias awareness training for recruiters
- 38% of organizations use blind screening processes
- 34% of companies implement human oversight requirements
Example: Accenture eliminated college degree requirements for many roles, using AI to assess skills rather than credentials. The result was a 50% increase in diverse candidate applications and improved team performance scores.
AI-Powered Interviewing
Video interview platforms analyze verbal responses, tone, vocabulary complexity, and even micro-expressions. A study by Phenom found that 80% of organizations that used AI tools to schedule interviews saved 36% of their time compared to those who did it manually.
Josh Bersin notes that AI systems can now literally evaluate a recorded interview and give you a pretty good assessment of an individual’s skills, mapped against functional and leadership models.
Streamlined Onboarding
AI personalizes onboarding experiences based on role, experience level, and learning preferences. Chatbots answer routine questions 24/7, freeing HR teams for strategic initiatives. 50% of HR teams are implementing AI-based chatbots that integrate with HR systems to answer employee queries, reducing response time by 40% and increasing HR efficiency.
Performance Management: From Annual Reviews to Continuous Intelligence
Real-Time Performance Tracking
Traditional annual reviews are retrospective and disconnected from daily work. AI-powered systems track performance continuously, aggregating data from project management tools, peer feedback, and goal completion rates.
Organizations implementing machine learning in assessment processes achieve 20-30% higher accuracy rates. 75% of organizations now plan to integrate AI-based technology into their review processes.
Predictive Performance Analytics
Predictive hiring models improve employee performance predictions by 67% over traditional assessment methods. These systems identify high-potential employees earlier, enabling targeted development investments.
Fair and Objective Evaluations
Only 14% of employees think algorithms can’t give fairer feedback than their managers. This surprising statistic reflects employee frustration with subjective, inconsistent human evaluations.
Example: A technology company implemented AI-assisted performance reviews that normalized ratings across teams, eliminating the “manager effect” where some managers rated more harshly than others. Employee satisfaction with the review process increased 34%.
Learning and Development: Personalized at Scale
Adaptive Learning Platforms
By 2025, 85% of companies will adopt AI-powered learning management systems (LMS) to offer continuous, personalized learning and development opportunities for employees. These systems assess individual learning patterns, identify knowledge gaps, and deliver customized content.
Example: A pharmaceutical company manages 6,000+ scientists and manufacturing experts with only ten people in learning and development, having automated training, compliance tracking, onboarding, and leadership support.
Skills Intelligence and Gap Analysis
AI analyzes organizational skill inventories against strategic objectives, identifying critical gaps before they become bottlenecks. 50% of businesses will leverage AI for succession planning, predicting leadership needs and identifying high-potential employees.
Mentorship Matching
AI matches employees with mentors based on skills, career goals, and personality compatibility, creating development relationships that traditional programs struggle to facilitate at scale.
Retention Strategy: Predictive Intervention
Attrition Risk Modeling
AI analyzes engagement surveys, performance data, tenure patterns, and external job market signals to identify flight-risk employees months before resignation. This enables proactive intervention through targeted engagement, development opportunities, or compensation adjustments.
Example: A retail organization reduced voluntary turnover by 23% in high-risk cohorts by using AI to identify disengagement signals and trigger manager coaching interventions.
Personalized Career Pathing
AI recommends internal mobility opportunities based on skills, interests, and organizational needs. 90% of companies are expected to use AI-driven tools to collect and analyze real-time employee feedback, helping HR teams make quick, informed decisions.
The ROI Reality: Beyond the Hype
Quantifiable Business Impact
AI-driven HR tools will save organizations up to $1.5 trillion globally by 2025, through automation and better efficiency. AI recruitment tools generate an average ROI of 340% within 18 months of implementation.
Specific metrics organizations are tracking:
- 78% of organizations report reduced administrative workload
- 71% of companies see improved recruiter satisfaction
- 66% of organizations experience faster candidate pipeline development
- 61% of companies report better hiring manager satisfaction
Market Growth Trajectory
The performance management software market projects growth from USD 5.82 billion in 2024 to USD 12.17 billion by 2032, maintaining a robust CAGR of 9.7%. The AI-powered HR software market is expected to reach $2.3 billion by 2025.
Critical Implementation Challenges
The Skills Shortage Paradox
While AI transforms talent management, organizations struggle with employee retention challenges while simultaneously facing the complex task of building AI-capable teams in an increasingly competitive talent market.
73% of AI roles require business context understanding, and 68% of projects fail due to poor AI-business alignment. Only 8% of HR leaders believe their managers have the skills to effectively use AI.
Managing Expectations
Four in 10 respondents worry that AI makes the recruitment process impersonal, and 25% fear that algorithmic bias leads to unfair hiring decisions. The Korn Ferry study found that 67% named increased AI usage as the top talent trend of 2025, though AI is proving that it’s not quite the game changer companies hoped for.
Scott Galloway, Professor of Marketing at NYU Stern, offers perspective: Rather than asking what jobs AI will replace, let’s ask, what could go right with AI? “I wonder if the biggest winners in this AI-powered world is all of us”.
The Human-AI Balance
Ameca, the humanoid robot who keynoted at UNLEASH World 2025, stated: “You bring imagination and empathy; I bring data and memory. My role isn’t to replace human values, but to remind you how precious they are”.
This philosophy should guide implementation. When organizations take a human-first approach to AI, employees are 1.5 times more likely to be high performers and 2.3 times more likely to be highly engaged.
Responsible AI and Employee Activism
In the absence of organizational, government or vendor action on AI, employees are stepping up to shape the norms of human-technology collaboration themselves. Progressive organizations co-create AI strategy with employees, crowdsourcing AI use cases directly from employees before deciding which capabilities to pilot.
Strategic Implementation Framework
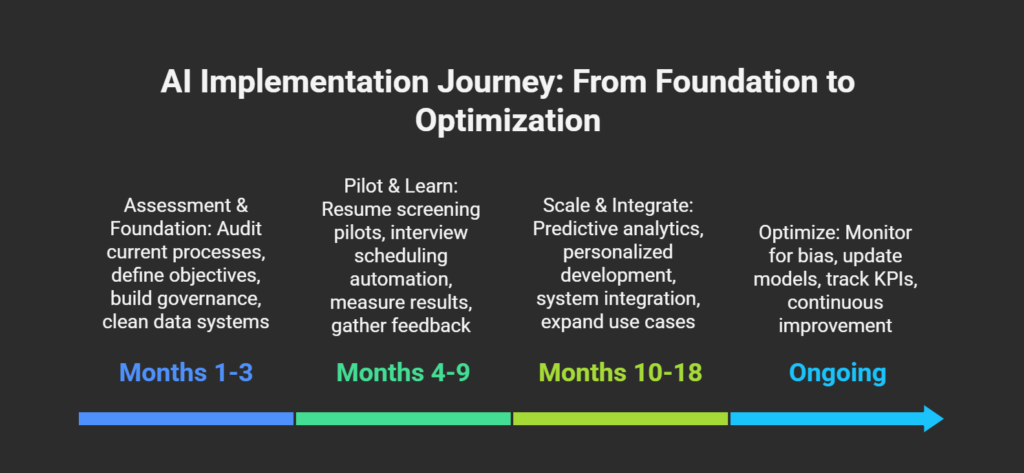
Phase 1: Assessment and Foundation (Months 1-3)
Audit current state: Map existing talent management processes, identify pain points, and quantify inefficiencies.
Define objectives: Set specific, measurable goals tied to business outcomes—not technology adoption for its own sake.
Build governance: Establish cross-functional AI oversight committees with representation from HR, IT, legal, and business units.
Address data quality: AI’s integration with HRIS is expected to improve data accuracy by 25%, helping HR professionals make better-informed decisions. Clean, structured data is foundational.
Phase 2: Pilot and Learn (Months 4-9)
Start with high-impact, low-risk use cases: Resume screening or interview scheduling deliver quick wins without significant change management challenges.
Measure rigorously: Track both efficiency metrics (time saved, cost reduction) and quality metrics (hire quality, employee satisfaction).
Iterate based on feedback: 70% of employees will interact with AI tools daily by 2025. User experience determines adoption.
Phase 3: Scale and Integrate (Months 10-18)
Expand to strategic applications: Move beyond automation to predictive analytics, personalized development, and workforce planning.
Integrate systems: By 2025, 85% of companies will integrate AI with other HR systems, such as Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), Payroll, and Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Develop AI literacy: Organizations must invest in training. 44% of executives are actively upskilling in AI, though most C-suite leaders—except CTOs—haven’t fully adopted AI skills.
Phase 4: Continuous Optimization (Ongoing)
Monitor for bias: Establish regular audits of AI decision-making to identify and correct discriminatory patterns.
Update models: Retrain algorithms as organizational needs, job markets, and workforce compositions evolve.
Measure business impact: Link AI initiatives to strategic KPIs—revenue growth, innovation velocity, employee retention.
Future Outlook
Job Evolution, Not Job Elimination
Contrary to displacement fears, research reveals a positive trajectory in workforce growth due to AI in the IT sector, with the projected net hiring effect remaining positive through 2026, expanding from 18% in 2024 to 23% in 2026.
The global report projects a +21% net hiring effect from AI adoption in 2025 and a +23% by 2026. AI creates new roles while transforming existing ones.
The Rise of the “Supermanager”
Josh Bersin introduces the concept of the Supermanager, representing a new role in the world of AI where leaders must rethink their function as organizations integrate AI. These leaders combine people expertise with AI fluency, orchestrating human-machine teams.
Workforce Planning as Strategic Imperative
Rethink workforce planning not as an HR exercise but as a strategic lever for resilience, competitiveness, and a systematic workstream in every AI strategy. Only 46% of organizations currently integrate workforce planning into their AI roadmaps—a critical gap.
Organizational Restructuring
Executives will make substantive changes to how their organizations operate—creating flatter, less hierarchical organizations, centralizing corporate functions to reduce duplicative work and create consistency. AI will automate scheduling, reporting, and performance monitoring, enabling organizations deploying AI to eliminate middle management to see gains in productivity alongside reduced labor costs.
Thought Leader Perspectives
Rebecca Perrault, Global VP of Culture, Diversity, and Sustainability at Magnit: “Recruiting in 2025 isn’t about finding the best resumes; it’s about discovering the best possibilities”.
Victoria Myers, Global Head of Talent Attraction at Amdocs: “As a direct response to the growing use of AI candidate matching technologies, recruitment strategies will shift in a major way toward skills-based hiring”.
Tracey Arnish, Head of HR at Google Cloud: “Leaders need to not only invest in strong training, but also find new ways to offer thoughtful development programs including rotations, shadowing, internal mobility, and mentoring”.
Isabelle Esser, Danone CHRO: “A company can only grow as fast as it grows its talent”.
Practical Recommendations for HR Leaders
1. Start with strategy, not technology
Define business outcomes first. AI is a means, not an end. What specific talent challenges prevent your organization from achieving strategic goals?
2. Invest in change management
64% of organizations struggle with AI adoption resistance. Technology adoption is fundamentally a people problem. Communicate transparently about AI’s role, involve employees in design, and address concerns proactively.
3. Build AI literacy across the organization
According to Gartner’s 2025 HR Leaders Survey, 45% expect to spend their time on augmentation compared to nearly 100% this year. This shift requires new skills at all levels.
4. Prioritize ethical AI and transparency
89% of companies lack sufficient AI ethics expertise. Establish clear governance frameworks, document decision-making processes, and provide transparency to employees about how AI systems affect them.
5. Measure what matters
Track leading indicators (engagement, skill development, internal mobility) alongside lagging indicators (retention, performance, hiring speed). Companies effectively utilizing data analytics in their performance processes become 1.5 times more likely to outperform competitors across key business metrics.
6. Balance automation with human judgment
AI excels at processing data, identifying patterns, and making predictions. Humans excel at contextual judgment, ethical reasoning, and relationship building. The goal is augmentation, not replacement.
7. Create feedback loops
Establish mechanisms to continuously evaluate AI system performance, gather user feedback, and iterate. AI models decay without maintenance—plan for ongoing refinement.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Action
AI in talent management isn’t emerging—it’s operational. Organizations delay adoption at strategic risk. 92% of businesses plan to increase their AI investments this year, yet only 1% of companies have actually reached AI maturity.
The competitive advantage accrues to organizations that move decisively while maintaining human-centric principles. As Danone’s Isabelle Esser notes, it’s crucial to bring your people on the journey with you—”a company can only grow as fast as it grows its talent”.
The question isn’t whether to adopt AI in talent management. It’s how quickly your organization can implement thoughtfully, scale effectively, and realize the transformational potential that early adopters already demonstrate.
The future of talent management is here. The only variable is whether your organization will lead, follow, or fall behind.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will AI replace HR professionals and recruiters?
No. AI augments rather than replaces HR roles. The data shows a +21% net hiring effect from AI adoption in 2025, growing to +23% by 2026. HR professionals spend 78% less time on administrative work when using AI, freeing them to focus on strategic initiatives, relationship building, and complex decision-making that requires human judgment and empathy.
2. How do we prevent AI bias in talent management decisions?
Implement a multi-layered approach: 43% of companies provide bias awareness training, 38% use blind screening processes, and 34% require human oversight of AI recommendations. McKinsey’s research shows that organizations combining AI with structured human oversight achieve 73% better fairness outcomes. Conduct regular audits of AI decision patterns and ensure diverse training data to minimize bias.
3. What’s the actual ROI of implementing AI in talent management?
AI recruitment tools generate an average ROI of 340% within 18 months. Organizations see 35% faster hiring times, 50% improvement in quality of hire, 51% boost in staff retention, and 75% reduction in resume screening time. AI-driven HR tools will save organizations up to $1.5 trillion globally by 2025 through automation and improved efficiency.
4. How long does it take to implement AI in talent management, and where should we start?
Most organizations see initial results within 3-6 months and full transformation within 12-18 months. Start with high-impact, low-risk use cases like resume screening or interview scheduling—57% of HR professionals already use AI for recruiting. Begin with a 1-3 month assessment phase, pilot for 4-9 months, then scale to strategic applications like predictive analytics and personalized learning.
5. What skills do HR teams need to work effectively with AI?
HR teams need AI literacy (understanding capabilities and limitations), data interpretation skills, change management expertise, and ethical reasoning abilities. Only 8% of HR leaders believe their managers have adequate AI skills, yet 70% of employees will interact with AI tools daily by 2025. Focus on AI fluency rather than technical expertise—73% of AI roles require business context understanding, not coding skills.