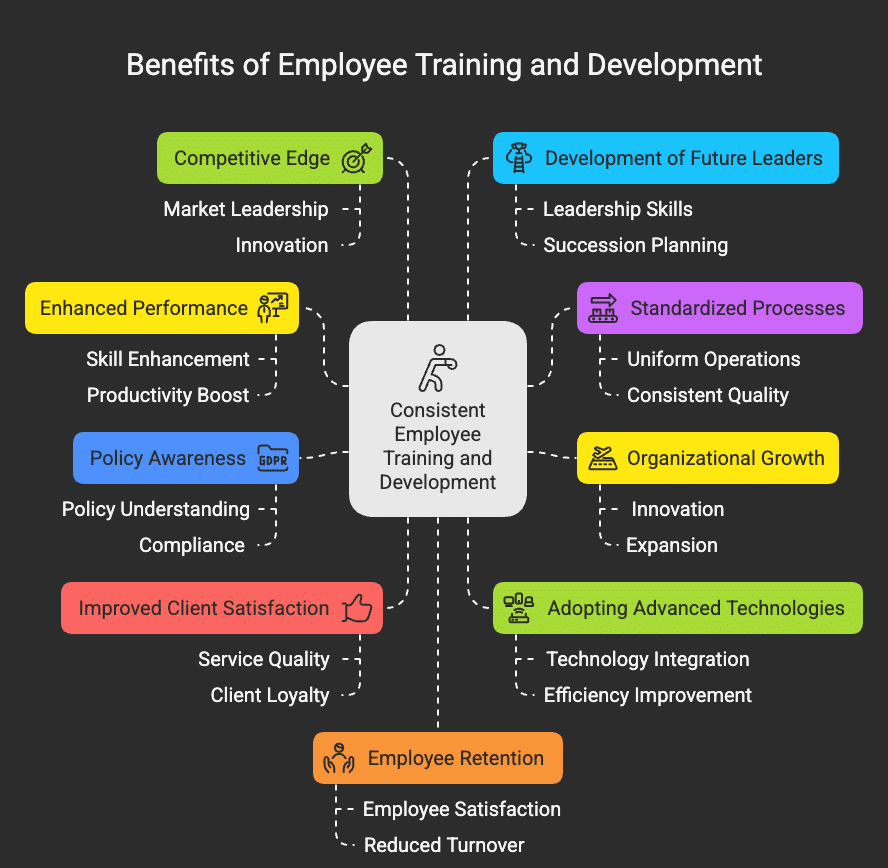
Have you ever wondered why your projects are always behind schedule or why your employees are losing interest in their work? A simple answer to this might be that employees at your workplace don’t have clear goals to direct them. Many organizations fail to understand the importance of goal setting, and as a result, they fail miserably.
TL;DR Summary
Clear goals provide direction, focus, and motivation, helping employees stay aligned with organizational objectives.
Key Benefits of Goal Setting
- Boosts employee motivation and accountability
- Helps in prioritizing work and improving time management
- Enhances decision-making and team collaboration
- Allows teams to measure success using SMART goals
- Acts as a roadmap for career growth
Types of Goals
Goals can be individual, team, or organizational—ideally linked to OKRs.
How Engagedly Helps
- SMART goal formulation
- Collaborative and transparent goal setting
- Real-time tracking and visibility
- Integration with performance management and actionable insights
Role of Managers
Managers guide, support, and provide feedback to help employees succeed.
Why are Goals important?
Goals are super important because they give you direction and purpose. Think of them like a map. Without a map, you’d just wander around, unsure of where you’re going, right? Goals work the same way—they help you focus on what you want to achieve and keep you motivated to get there.
Plus, they give you something to measure your progress against, so you can see how far you’ve come and what you still need to work on.
Setting goals also helps you prioritize what’s important. In a busy world, it’s easy to get distracted by all the little things, but goals keep you on track toward what really matters.
And whether it’s personal or professional, having a clear goal gives you that sense of accomplishment when you hit it, which just feels amazing!
So, in a nutshell, goals are your guideposts—they keep you focused, motivated, and give you a reason to celebrate when you achieve them.
Importance of Goal Setting
Goal setting provides a sense of direction and focus, which helps in altering the behaviors and attitudes required to accomplish the objectives. It gives you momentum and a thrust that pushes you in the direction of self-mastery to improve every day and be resilient in challenging times.
Goal-setting benefits not only the employee but the organization as a whole. Considering the importance of goal setting, a good amount of time should be devoted to it. In this article, we will discuss why goal-setting is important for your employees.
Also to learn more about how to establish clear and achievable employee goals, check out this detailed guide
1. Motivates Employees
Goal setting keeps employees motivated by fostering a culture of accountability and progress tracking. It enables employees to stay focused and aligned with the company’s strategic objectives, resulting in improved overall organizational performance.
Goal setting serves as a powerful tool to not only communicate expectations but also to illustrate the broader impact of your team’s efforts. This fosters higher engagement, motivation, and productivity, ultimately fueling significant company growth.
Also Read: Chasing Goals When Motivation Is Low
2. Prioritizing Work
Having a clear goal in mind helps in focusing on priorities. Once the goals are decided, they can be taken up for completion in order of their priorities. This allows tasks to be completed on time and in a logical order. The ability to prioritize goals shows an employee’s ability to plan and focus ahead. This makes them better prepared and clear on what work needs to be completed and by when.
3. Decision Making
Goals help in enhancing the decision-making skills of the employee. They serve as a guide in the decision-making process. Before taking any decision, an employee will evaluate it against the goal that they are trying to achieve. Every decision is taken based on the outcome of the decision.
Similarly, this applies at an organizational level, where every decision is taken thinking about how it will affect the business. Goals are useful for employees when they come across challenging projects as they helps in making wise decisions.
Also Read: 3 Factors To Remember When Setting Employee Goals
4. Teamwork
When individual goals are linked to organizational goals, it promotes teamwork. The leaders and managers must let every employee know how their goal is linked to the organization’s goal. The employee will understand the importance of teamwork once they know how they fit in the overall organizational goal and how their goal is linked to their peers.
5. Measure Success
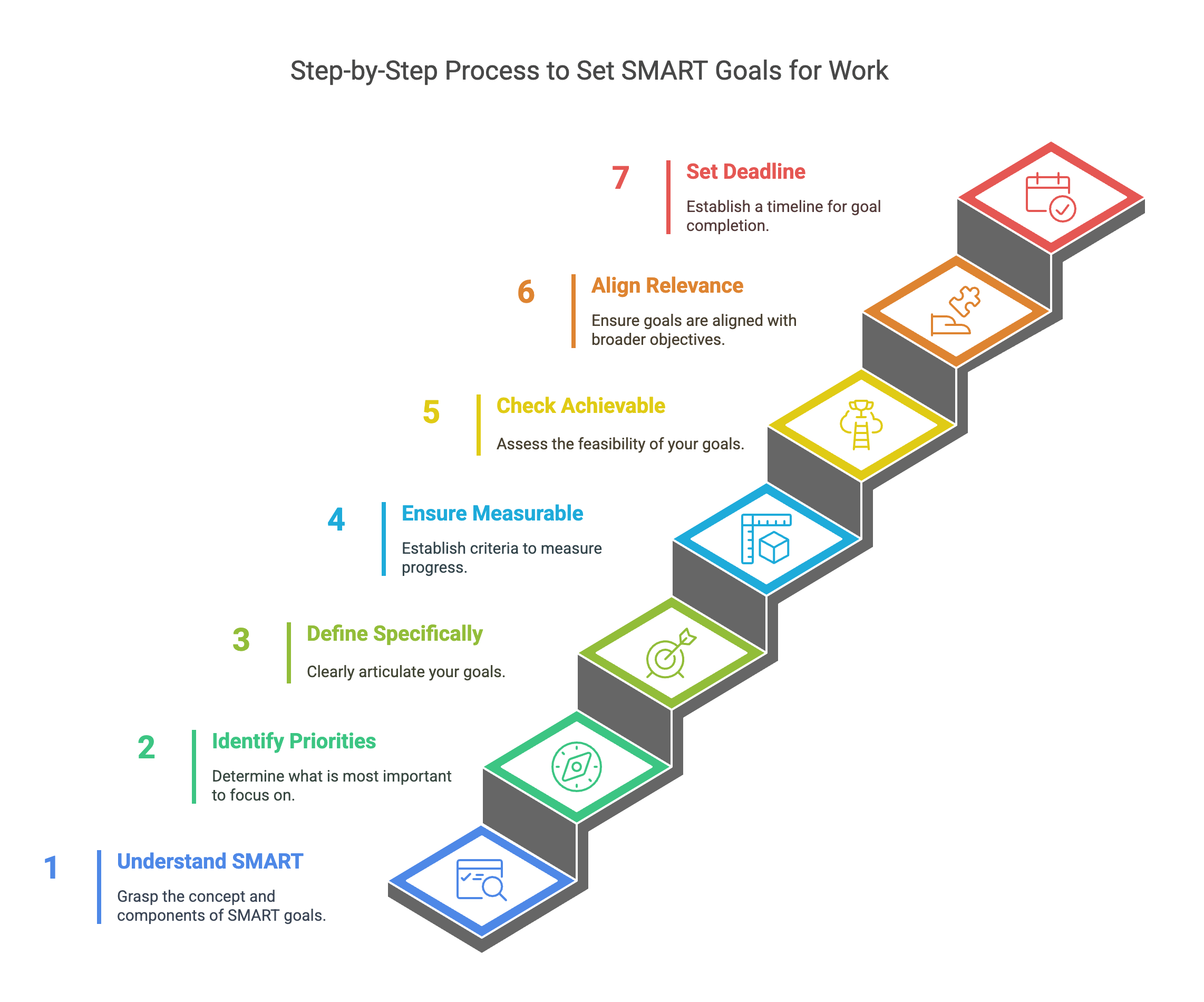
When goal setting is done correctly, it will help in measuring employee and organization success. The ‘SMART‘ way could be used to set a goal so that they can be measured quantitatively as well as qualitatively. The SMART method stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
For employees, a successful goal should be a specific one for which progress can be measured and achievable on time. Measurable goals will help everyone evaluate the results and help them know what was effective. This applies to all business processes—from how teams create paystubs to how they develop new products—providing quantifiable metrics for success.
6. Guides Employees
Goals setting guides employees in moving forward in the organization. It acts as a roadmap for the employee towards achieving what they want.
For example, if an employee wants to become a CEO someday, writing down that goal with details on what steps they will take to achieve it, can help them with the goal. Properly thought and stated goals will not only guide the employee continuously but will help in improving the skills and capabilities of the employees.
7. Time Management
If you want to improve how you manage time – stop doing what doesn’t need to be done! -Peter Drucker.
Time is one of the most important resources for every business. Having a clear goal in place will help employees to manage their time effectively. Goals help in prioritizing work and prevent employees from working on irrelevant things and getting distracted.
For example: When you have a deadline for a web application project, setting specific goals for each module of the project will help you finish the project on time and eliminate distractions.
Also Read: Engagedly For Managing Your Remote Team: Goal Setting And OKRS
Enhancing Organizational Performance Through Effective Goal Setting with Engagedly
Setting clear, achievable goals is pivotal for organizational success. It provides a roadmap for action, aligns individual efforts with company objectives, and fuels motivation and engagement. However, traditional goal-setting methods often lack agility, transparency, and collaborative input, hindering their effectiveness.
This is where Engagedly steps in, offering a comprehensive platform that elevates goal setting to a strategic level. Engagedly empowers organizations to:
1. Foster SMART Goal Formulation
- Guidance and Tools: Engagedly provides resources and frameworks to assist in crafting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals. This ensures clarity, focus, and alignment with organizational aspirations.
- Cascading Objectives: Break down overall objectives into smaller, attainable goals for individual teams and employees. This fosters ownership, engagement, and a clear understanding of how individual contributions impact the bigger picture.
2. Facilitate Collaborative Goal Setting
- Interactive Platform: Engagedly encourages collaborative goal setting, allowing managers and employees to work together in defining objectives. This promotes open communication, buy-in, and a sense of shared responsibility for success.
- Continuous Feedback Loop: Engagedly’s features facilitate ongoing feedback on goals, enabling adjustments and refinements as circumstances evolve. This maintains agility and ensures focus on the most impactful objectives.
3. Enhance Goal Visibility and Tracking
- Real-Time Monitoring: Engagedly’s intuitive platform provides real-time visibility into individual and team goal progress. This fosters accountability, allows for course correction, and empowers teams to celebrate milestones along the way.
- Transparent Goal Sharing: Engagedly promotes transparency by making goals visible across the organization. This fosters a sense of shared purpose, collaborative efforts, and heightened motivation to achieve collective aspirations.
4. Optimize Performance Management
- Seamless Integration: Engagedly seamlessly integrates goal setting with performance reviews and development plans. This ensures alignment, clarity, and a holistic understanding of how goals contribute to individual and organizational growth.
- Data-Driven Insights: Track goal progress and analyze data to identify patterns and trends. This allows for informed decision-making, continuous improvement of goal-setting practices, and data-driven adjustments for future success.
Engagedly goes beyond mere goal setting. It provides a robust platform that empowers organizations to translate aspirations into tangible results by driving strategic alignment, fostering collaboration, and providing valuable insights through continuous monitoring and feedback.
If you want to explore practical steps to set and achieve goals in your organization, check out our blog on setting workplace goals and making them happen here.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the importance of goal setting?
Goals are important because they provide clarity, motivation, measurement, accountability, and a sense of achievement. They provide a clear roadmap for where one wants to go and what one wants to achieve.
By setting specific goals, individuals and teams can stay focused and motivated on what matters most, allowing them to work towards their desired outcomes with a sense of purpose and direction
Q2. How can goals improve workplace productivity?
Ans. By setting clear goals and objectives, individuals and teams can prioritize their work, reduce distractions, and stay focused on what matters most. This can lead to increased productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
Q3. How can managers help employees set and achieve goals?
Ans. Managers can help employees set and achieve goals by providing clear expectations, regular feedback, and opportunities for growth and development. They can also offer support and guidance to help employees overcome obstacles and achieve their desired outcomes.
Q4. How can individuals and teams stay motivated when working towards goals?
Staying motivated requires a sense of purpose and a clear understanding of how achieving goals will contribute to overall success. Regular feedback and recognition can also be highly motivating, as can a supportive and collaborative work environment.



 A matrix organization is a management method that integrates both functional and project-oriented approaches. The matrix structure involves dual reporting lines, where the staff members usually report to both a functional manager, who supervises their skills development in a specific department or discipline, and a project manager, who directs them to realize the project’s goals and deadlines.
A matrix organization is a management method that integrates both functional and project-oriented approaches. The matrix structure involves dual reporting lines, where the staff members usually report to both a functional manager, who supervises their skills development in a specific department or discipline, and a project manager, who directs them to realize the project’s goals and deadlines.