Here’s a reality check: The average voluntary turnover rate in the U.S. sits at 13.5% as of 2025, and 51% of U.S. employees, roughly 1 in 2 workers, are either actively searching for or watching for new job opportunities. That’s not just a statistic. That’s half your workforce with one foot out the door.
But here’s what makes this even more concerning: most of this turnover is preventable. Research shows that roughly 75% of voluntary employee turnover can actually be avoided.
The question isn’t whether employees are leaving—it’s why they’re leaving, and what you can do about it before your best talent walks out the door.
The Cost of Getting This Wrong
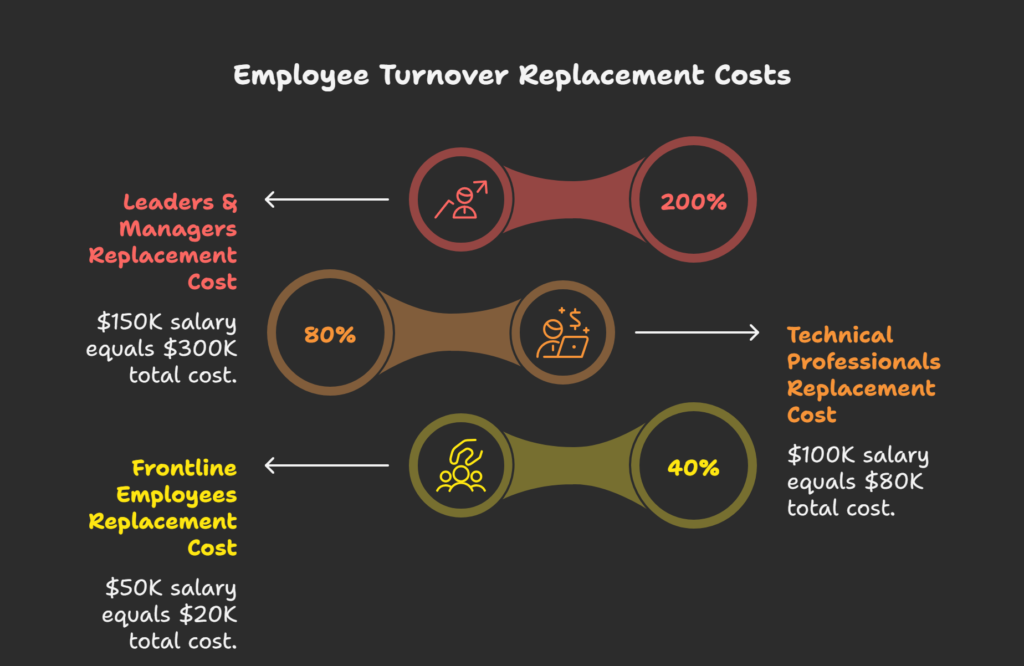
Before we dive into solutions, let’s talk numbers. Studies estimate that replacing an employee can cost about 33% of their annual salary. For a mid-level employee earning $60,000, that’s nearly $20,000 down the drain—and that’s just the direct costs.
The real damage? Lost productivity, decreased team morale, knowledge gaps, and the strain on remaining employees who have to pick up the slack while you scramble to fill the position.
Why Do Employees Leave Their Jobs? The Top 8 Reasons (And They’re Not What You Think)
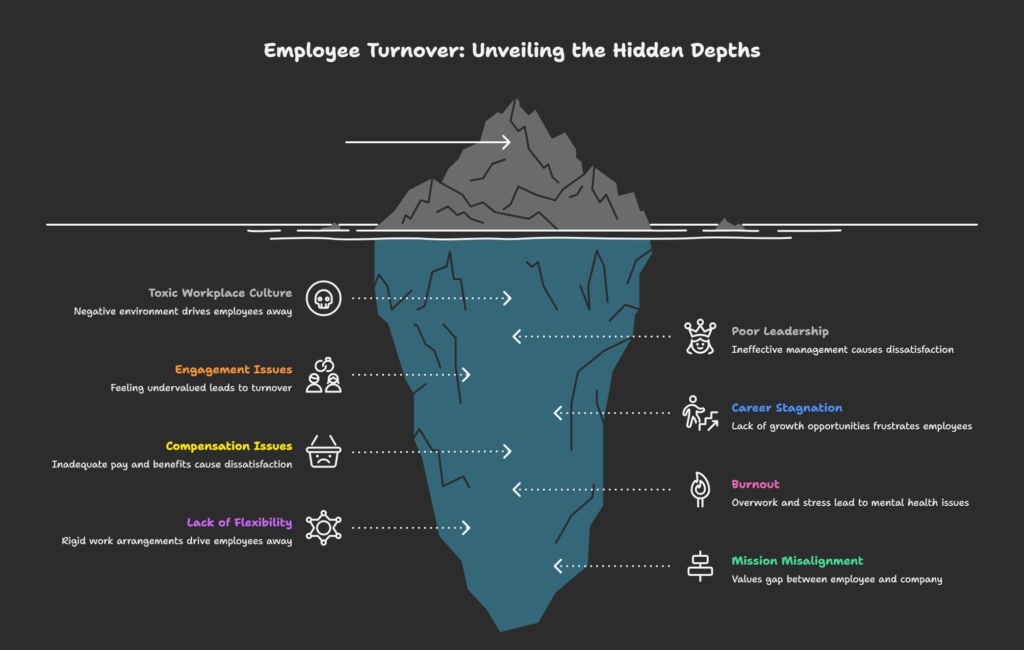
1. Toxic Workplace Culture: The Silent Killer
Let’s start with the elephant in the room. A staggering 32.4% of individuals who left a position within the past year cited a toxic or negative workplace as one of their reasons for resigning, making it the most commonly reported factor.
Here’s the kicker: Only 15.3% of employers surveyed thought that employees had left due to a toxic workplace environment.
Read that again. Leadership is either completely unaware of the toxicity or unwilling to address it.
What does a toxic workplace look like in practice?
- Lack of psychological safety where employees can’t speak up
- Office politics that reward favoritism over performance
- Blame culture where mistakes aren’t learning opportunities
- Gossip, cliques, and exclusionary behavior
- Disrespect from colleagues or leadership
What HR Can Do: Conduct anonymous culture audits quarterly. Use pulse surveys to gauge the real temperature of your workplace. But here’s the critical part—you must act on the feedback. Employees stop giving honest feedback when they see it disappear into a void.
Create clear channels for reporting toxic behavior with guaranteed protection from retaliation. Train managers on recognizing and addressing toxic dynamics before they become resignation catalysts.
2. Poor Leadership and Management: People Don’t Quit Jobs, They Quit Bosses
You’ve heard this before, and it’s still true. Gallup research consistently finds that 50% of employees who quit do so because of their manager.
The second most frequent factor among job quitters was poor company leadership, and the third most frequent was conflict with a manager or supervisor. Combined, these paint a clear picture: employees aren’t quitting jobs—they’re quitting bad leadership.
Bad managers manifest in several ways:
- Micromanagement that suffocates autonomy
- Inconsistent or unclear communication
- Failure to provide feedback or recognition
- Playing favorites or showing bias
- Not advocating for their team’s growth
Real-World Example: Sarah, a marketing specialist, consistently exceeded her targets for 18 months. Her manager took credit for her campaigns in leadership meetings and never acknowledged her contributions. When a competitor offered her 10% less than her current salary but with a manager who valued transparency and recognition, she left without hesitation.
What HR Can Do: Invest heavily in leadership development—not just once during onboarding, but continuously. Train managers on:
- Conducting effective one-on-ones
- Giving meaningful feedback
- Recognizing contributions authentically
- Delegating with trust, not just dumping tasks
Implement 360-degree feedback so managers understand how their leadership style impacts retention. Make management effectiveness a key metric in performance reviews, not just business outcomes.
3. Compensation and Benefits: The Foundation That Can’t Be Ignored
Yes, money matters. While it’s not the only reason employees leave, it’s still foundational. Among the top reasons cited for leaving, pay/benefits accounts for 11% of departures.
But here’s what’s changed: employees are smarter about total compensation. They’re not just looking at salary—they’re evaluating:
- Healthcare benefits and mental health coverage
- Retirement contributions and matching
- Flexible spending accounts
- Student loan repayment assistance
- Equity or profit-sharing opportunities
What HR Can Do: Conduct regular compensation benchmarking against industry standards. Use tools like Engagedly to track pay equity across departments, ensuring you’re competitive not just at hiring but throughout employment.
Be transparent about pay structures. Salary secrecy breeds resentment. Create clear career ladders that show employees exactly what they need to do to reach the next compensation level.
Don’t wait for annual reviews to adjust compensation. If someone’s role has expanded or they’ve taken on additional responsibilities, adjust their pay accordingly—before they start interviewing elsewhere.
4. Career Stagnation: Nowhere to Go But Out
Research shows that 43% of employees planning to leave prioritize training and development, compared to just 31% who intend to stay long-term.
When employees feel stuck, they leave. It’s that simple.
Career stagnation looks like:
- No clear path for advancement
- Skills are becoming outdated, with no training opportunities
- Doing the same tasks for years without new challenges
- Watching external hires fill senior positions repeatedly
- Lack of mentorship or stretch assignments
What HR Can Do: Create Individual Development Plans (IDPs) for every employee—not just high potentials. Use performance management platforms like Engagedly to track skill development, identify learning opportunities, and align career goals with business needs.
Implement job rotation programs, cross-functional projects, and lateral moves that keep work engaging. Sometimes career growth isn’t just about climbing up—it’s about expanding horizontally to build diverse skills.
Establish mentorship programs that connect junior employees with senior leaders. The ROI? Higher engagement, better succession planning, and employees who feel invested in.
5. Burnout and Work-Life Imbalance: The Breaking Point
Burnout rates are now at a record high of 70% and nearly half of U.S. workers are suffering from mental health issues.
This isn’t just about being busy. Burnout is a state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged stress, and it’s driving employees out the door faster than almost anything else.
Warning signs include:
- Consistently working beyond normal hours
- No clear boundaries between work and personal time
- Unrealistic deadlines and expectations
- Insufficient staffing leading to overwork
- Lack of support for mental health
What HR Can Do: Move beyond offering an EAP (Employee Assistance Program) that nobody uses. Create a culture where taking time off is encouraged, not just permitted.
Implement mandatory “unplug” policies. Some companies are experimenting with “no meeting Fridays” or blocking out focus time in calendars company-wide.
Train managers to spot burnout symptoms early. Create workload distribution visibility so leadership can see when teams are consistently overextended.
Most importantly: model the behavior from the top. If your executives are sending emails at midnight and working weekends, your policies around work-life balance are just performative.
6. Lack of Recognition and Feeling Undervalued
Engagement and culture accounts for 37% of reasons employees cite for leaving, the highest category.
Recognition isn’t about pizza parties or generic “employee of the month” plaques. It’s about feeling seen, valued, and appreciated for your specific contributions.
Employees leave when:
- Their ideas are consistently ignored or shot down
- Achievements go unacknowledged
- Feedback is only given when something goes wrong
- There’s no connection between their work and company’s success
- Compensation doesn’t reflect increased responsibilities
What HR Can Do: Build recognition into your daily operations, not just annual reviews. Use continuous performance management systems that enable peer-to-peer recognition, manager kudos, and linking achievements to company objectives.
Create multiple recognition channels:
- Real-time acknowledgment in team meetings
- Written recognition in company communications
- Monetary rewards tied to specific achievements
- Public celebration of wins
- Private, personalized thank-yous from leadership
The key is specificity. “Great job” means nothing. “Your analysis of the Q3 data revealed a trend we hadn’t noticed, which directly led to a 15% increase in customer retention” means everything.
7. Flexibility and Remote Work: The New Non-Negotiable
The pandemic permanently shifted expectations. Pew Research Center reports that 75 percent of adults in jobs that can be done from home are working remotely at least some of the time.
Rigid return-to-office mandates are causing resignations. Employees have proven they can be productive remotely, and many are unwilling to give up the benefits:
- No commute (saving time and money)
- Better work-life integration
- Reduced stress and improved well-being
- Ability to relocate to lower cost-of-living areas
What HR Can Do: Get granular about flexibility needs. Not every role can be fully remote, but most can offer some flexibility. Options include:
- Hybrid schedules with core collaboration days
- Flexible start/end times
- Compressed workweeks (4×10 schedules)
- Remote work from anywhere policies
- Results-based performance metrics instead of hours-logged tracking
Nearly 55 percent of employees said they’d be more likely to stay with an employer that offered flextime. This isn’t a perk anymore—it’s a retention strategy.
8. Mission and Purpose Misalignment: The Values Gap
Today’s workforce, especially younger generations, wants their work to matter. They want to work for companies whose values align with their own.
Employees leave when:
- Company values are just words on a wall with no action behind them
- The mission feels hollow or purely profit-driven
- Ethical concerns go unaddressed
- There’s no clear connection between daily work and the company’s purpose
- Social responsibility and sustainability are ignored
What HR Can Do: Be authentic about your mission. If your company exists to make money, own it—but find ways to create meaning within that framework through customer impact, innovation, or team development.
Regularly communicate how individual contributions connect to larger goals. Use town halls, internal newsletters, and one-on-ones to draw those connections explicitly.
Create opportunities for employees to engage in work that aligns with their values—whether that’s volunteering initiatives, sustainability projects, or innovation labs working on meaningful problems.
The Great Detachment: A Warning Sign for 2025
Here’s something that should terrify every HR leader: U.S. employee engagement reached an 11-year low, indicating that many workers feel disconnected even in their new roles.
We’ve moved from the Great Resignation to what experts are calling the “Great Detachment”—employees aren’t necessarily leaving, but they’re mentally checked out. This is arguably worse because:
- Productivity tanks
- Innovation disappears
- Customer experience suffers
- The disengagement becomes contagious
- When the economy shifts, these disengaged employees will leave en masse
What HR Leaders Need to Do Right Now
1. Implement Stay Interviews, Not Just Exit Interviews
By the time you’re conducting an exit interview, it’s too late. Stay interviews—regular conversations with current employees about what keeps them engaged and what might cause them to leave—are proactive retention tools.
Ask questions like:
- “What would make you consider leaving?”
- “What do you look forward to when you come to work?”
- “What frustrates you most about working here?”
- “What would you change if you could?”
2. Use Data to Predict Flight Risks
Leverage HR analytics to identify patterns in turnover. Look at:
- Time in role before departure
- Performance ratings vs. attrition
- Manager-specific retention rates
- Department-level trends
- Engagement survey correlations
Modern platforms like Engagedly provide predictive analytics that can flag potential flight risks based on engagement scores, performance trends, and other signals—giving you time to intervene.
3. Hold Managers Accountable for Retention
Make retention a key metric in manager performance reviews. Track:
- Team turnover rates
- Employee engagement scores
- Development plan completion
- Stay interview frequency
- Recognition frequency
Managers with consistently high turnover should receive additional support, or if cultural problems persist, be moved out of leadership positions.
4. Create Transparent Career Pathways
Map out clear career progression frameworks for every role in your organization. Employees should be able to answer:
- “What’s the next step in my career here?”
- “What skills do I need to develop?”
- “What’s the timeline for advancement?”
- “What does success look like at the next level?”
5. Invest in Continuous Learning
Without clear growth pathways, employees are likely to look elsewhere for career advancement. Build a learning culture through:
- Tuition reimbursement or assistance programs
- Internal training and certification opportunities
- Conference attendance and professional development budgets
- Lunch-and-learns and knowledge sharing
- Stretch assignments and special projects
6. Fix Your Onboarding
29% of survey respondents shared they quit a job within 90 days of starting. That’s nearly a third of new hires not making it past the first quarter.
Your onboarding is either a retention tool or a resignation catalyst. Invest in:
- Structured 30-60-90 day plans
- Regular check-ins during the first 6 months
- Buddy systems for new hires
- Clear role expectations and success metrics
- Early wins and meaningful work from day one
The Bottom Line: Retention Is a Continuous Strategy, Not a One-Time Fix
Why do employees leave their jobs? Organizations fail to meet their evolving needs for respect, growth, flexibility, recognition, and purpose.
The companies that win the talent war in 2025 and beyond won’t be the ones with the flashiest perks or the highest salaries (though competitive compensation is table stakes). They’ll be the ones that:
- Create psychologically safe cultures where people can thrive
- Develop managers into leaders worth following
- Provide clear pathways for growth and development
- Recognize and value contributions authentically
- Offer flexibility that respects employees’ lives outside work
- Connect daily work to a meaningful purpose
Given that approximately 42% of turnover is viewed as preventable by the employees themselves, there’s an enormous opportunity for HR intervention.
The question is: Will you wait until your best employees hand in their resignations, or will you act now to build the kind of workplace people want to stay in?
Your turnover rate is a report card on your organizational health. What grade are you currently getting?